Now Reading: Everything You Need to Know About Coconut Milk
-
01
Everything You Need to Know About Coconut Milk
Everything You Need to Know About Coconut Milk
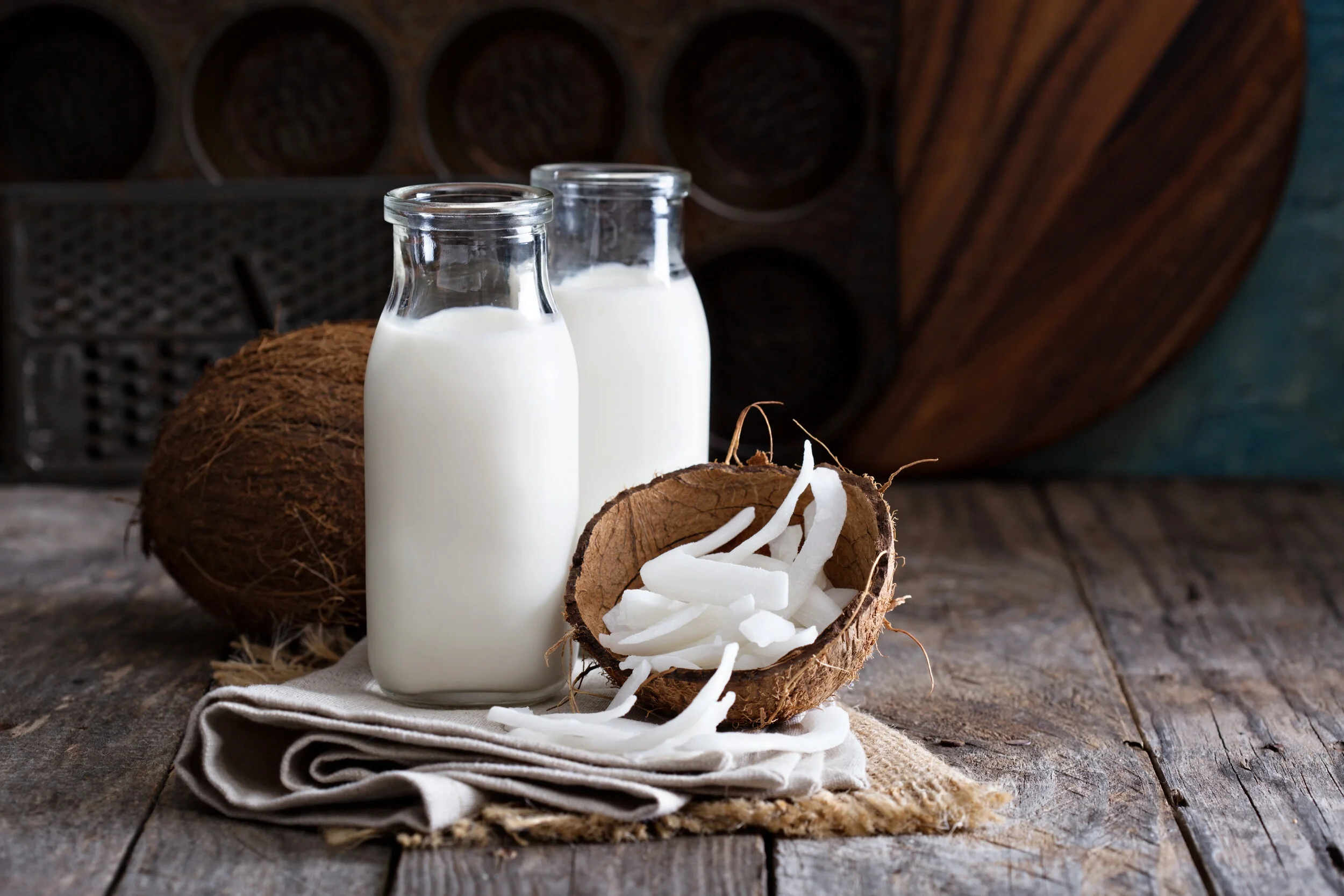

Have you ever wondered about the creamy, white liquid that adds a tropical twist to so many dishes? That’s coconut milk, a versatile and delicious ingredient that has found its way into kitchens all over the world. From rich curries to refreshing smoothies and even decadent desserts, it offers a unique flavor and texture that is hard to resist. This plant-based milk is not just for cooking; it’s a staple in many cultures and a popular dairy alternative for those following vegan or lactose-free diets.
This guide will explore the wonderful world of coconut milk. We’ll cover what it is, how it’s made, its nutritional benefits, and the different types you can find at the store. We will also share creative ways to use it in your daily meals and answer some common questions you might have. Get ready to discover why this humble ingredient deserves a permanent spot in your pantry.
Key Takeaways
- What It Is: Coconut milk is a plant-based liquid made from the grated flesh of a mature coconut, not to be confused with coconut water.
- Types: It comes in various forms, including canned (full-fat and light), refrigerated cartons (for drinking), and powdered, each suited for different uses.
- Health & Nutrition: It contains beneficial fats called MCTs, along with vitamins and minerals. Moderation is key due to its high saturated fat content.
- Culinary Uses: Extremely versatile, it’s a key ingredient in savory dishes like curries and soups, as well as sweets, baked goods, and beverages.
- Dairy-Free Alternative: It is an excellent substitute for dairy milk or cream for individuals who are lactose intolerant, vegan, or have milk allergies.
What Exactly Is Coconut Milk?
It’s easy to get confused between the different liquids that come from a coconut, but coconut milk is distinct. It is not the clear liquid you find when you crack open a fresh, young coconut—that’s coconut water. Instead, coconut milk is a man-made product created by processing the white flesh of mature, brown coconuts.
The process is quite simple. The coconut flesh is finely grated or shredded and then steeped in hot water. The cream that rises to the top is skimmed off; this is the thickest, richest form of coconut milk. The remaining liquid is then squeezed through a cheesecloth to extract a thinner liquid. The first press yields a thick milk, while subsequent presses produce a thinner version. Most commercial products blend these liquids with water to achieve a specific consistency and fat content. This process gives it its signature opaque, milky-white appearance and rich, creamy texture.
A Brief History of Coconut Milk
Coconuts have been a vital source of food and resources for thousands of years, particularly in tropical regions across Asia, Africa, and Latin America. The use of coconut milk is deeply embedded in the culinary traditions of these areas. In Southeast Asian cuisines, like Thai and Filipino, it is the foundation for countless curries, stews, and desserts. In India, it’s a staple in coastal dishes, providing a cooling balance to spicy flavors.
Its journey to Western countries is more recent. As global travel and cultural exchange expanded, so did the demand for international ingredients. Today, coconut milk is a mainstream product found in virtually every supermarket in the United States, celebrated for its flavor and its role as a plant-based alternative to dairy.
The Different Types of Coconut Milk
Walking down the grocery aisle, you might notice several different kinds of coconut milk. They vary in consistency, fat content, and intended use. Understanding the differences will help you choose the right one for your recipe.
Canned Coconut Milk
This is the most common type used for cooking and baking. It’s typically found in the international foods aisle and comes in a can. It has a high fat content, which makes it thick and creamy—perfect for adding richness to dishes.
- Full-Fat: This version is rich and luscious. When you open a can that has been sitting for a while, you’ll often see a solid, thick layer of coconut cream on top with a thinner liquid underneath. This separation is natural. The cream is fantastic for whipping or creating extra-rich sauces. Full-fat coconut milk is ideal for traditional curries and soups where a velvety texture is desired.
- Light (or Lite): This is simply full-fat coconut milk that has been diluted with more water. It has fewer calories and a lower fat content, resulting in a thinner consistency. It works well in recipes where you want the coconut flavor without the heavy richness, such as in lighter soups or as a liquid for cooking rice.
Refrigerated Coconut Milk Beverage
Found in the dairy aisle next to almond and soy milk, this type of coconut milk is specifically designed for drinking. It is significantly more diluted than its canned counterpart, giving it a consistency similar to cow’s milk. It’s often fortified with vitamins like D and B12 and calcium to make it a more comparable nutritional substitute for dairy milk. It’s perfect for pouring over cereal, adding to coffee, or blending into smoothies. However, due to its thinness, it’s not a good substitute for canned coconut milk in most cooking applications.
Coconut Milk Powder
Coconut milk powder is dehydrated coconut milk. It’s a convenient, shelf-stable option that allows you to control the consistency. To use it, you simply mix the powder with hot water. Use less water for a thick, creamy milk suitable for curries, or add more water for a thinner milk perfect for drinking or soups. It’s a great choice for those who use coconut milk infrequently and want to avoid waste.
Nutritional Profile of Coconut Milk
The nutritional content of coconut milk can vary widely depending on the type and brand. Canned, full-fat versions are more calorie-dense, while refrigerated beverages are much lighter. Here, we’ll focus on the general profile of traditional, unsweetened canned coconut milk.
It is primarily a source of calories from fat, specifically saturated fat. However, the type of fat is what makes it interesting. A large portion of the fat in coconuts comes from medium-chain triglycerides, or MCTs. Unlike the long-chain fatty acids found in many other foods, MCTs are metabolized differently by the body. They are transported directly from the gut to the liver, where they can be used as a quick source of energy.
Beyond fats, coconut milk also provides small amounts of essential minerals.
|
Nutrient (per 1/2 cup, approx. 120g) |
Full-Fat Canned |
Light Canned |
Refrigerated Beverage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Calories |
~220 |
~75 |
~25 |
|
Fat (g) |
~24 |
~7 |
~2.5 |
|
Saturated Fat (g) |
~21 |
~6 |
~2.5 |
|
Carbohydrates (g) |
~3 |
~2 |
~1 |
|
Protein (g) |
~2 |
~0.5 |
~0 |
|
Manganese (% DV) |
~50% |
~17% |
Varies (often fortified) |
|
Copper (% DV) |
~16% |
~5% |
Varies (often fortified) |
|
Iron (% DV) |
~11% |
~4% |
Varies (often fortified) |
Note: Values are approximate and can vary by brand. DV = Daily Value.
Potential Health Benefits
When consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet, coconut milk may offer some health advantages.
Source of Quick Energy
The MCTs in coconut milk are a unique type of fat. Because they are processed quickly by the liver, they provide a rapid energy source for your body and brain. This makes them less likely to be stored as body fat compared to other types of fats. Athletes sometimes use MCTs for a quick performance boost.
May Support Weight Management
Some studies suggest that the MCTs in coconut products can help with weight management. They may promote a feeling of fullness (satiety), which can lead to a lower overall calorie intake. Additionally, the body uses more energy to digest MCTs compared to long-chain fats, potentially giving a slight boost to your metabolism.
A Note on Saturated Fat
It is important to address the high saturated fat content in coconut milk. For decades, dietary guidelines have recommended limiting saturated fat intake. However, recent research is exploring whether the source of the saturated fat matters. The primary saturated fat in coconuts is lauric acid, an MCT. The effects of lauric acid on heart health are still a topic of scientific debate. While some studies suggest it may raise “good” HDL cholesterol, it can also raise “bad” LDL cholesterol. Therefore, experts advise enjoying full-fat coconut milk in moderation within a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. For more in-depth articles on nutrition and wellness, you can explore resources like Forbes Planet.
Cooking with Coconut Milk: A Culinary Workhorse
The true magic of coconut milk comes alive in the kitchen. Its ability to add creaminess, subtle sweetness, and a rich body to dishes is unparalleled.
In Savory Dishes
This is where canned coconut milk truly shines. It forms the base of countless iconic meals.
- Curries: Thai green, red, and yellow curries all rely on coconut milk to create their signature creamy sauce and balance the intense flavors of curry paste, chiles, and herbs.
- Soups: A splash can transform a simple vegetable or lentil soup into a velvety, satisfying meal. It’s a key ingredient in Thai Tom Kha Gai (coconut chicken soup).
- Stews and Braises: Use it as a braising liquid for chicken, fish, or tofu. It tenderizes the protein while infusing it with a delicate coconut flavor.
- Sauces: Create a simple, delicious sauce for noodles or steamed vegetables by simmering coconut milk with ginger, garlic, and a splash of soy sauce.
In Sweet Treats and Desserts
The rich texture of coconut milk makes it a natural fit for desserts.
- Puddings and Custards: It can be used to make classic desserts like chia seed pudding or a creamy coconut panna cotta.
- Ice Cream: It serves as an excellent base for dairy-free ice cream, creating a finished product that is just as creamy as traditional versions.
- Baked Goods: Substitute it for regular milk in recipes for cakes, muffins, and quick breads to add moisture and a hint of coconut flavor.
In Beverages
Refrigerated coconut milk is your go-to for drinks.
- Smoothies: It adds creaminess and a tropical note to any fruit or green smoothie.
- Coffee and Tea: Use it as a creamer in your morning coffee or to make a dairy-free latte or chai.
- Hot Chocolate: Create a rich and decadent hot chocolate by warming coconut milk with cocoa powder and a sweetener of your choice.
How to Choose and Store Coconut Milk
Choosing the right coconut milk is simple once you know what to look for. For cooking, look for canned varieties with minimal ingredients—ideally just coconut and water. Some brands add guar gum as a stabilizer, which is fine and helps prevent separation. Avoid products with added sugars unless a recipe specifically calls for sweetened coconut cream.
When buying canned coconut milk, shake the can. If you don’t hear any sloshing, it means the cream has solidified at the top, which is a sign of a high-quality, high-fat product.
Storage Tips:
- Unopened Cans/Cartons: Store in a cool, dark pantry. They are shelf-stable for a long time.
- Opened Canned Milk: Do not store it in the can. Transfer any leftover coconut milk to an airtight glass or plastic container and refrigerate. It will last for about 4 to 6 days.
- Opened Refrigerated Milk: Keep it in its original carton in the fridge and use it by the date printed on the package, usually within 7 to 10 days of opening.
- Freezing: You can freeze leftover coconut milk in an ice cube tray. The frozen cubes are perfect for adding to smoothies or dropping into a simmering soup. Note that the texture may change slightly upon thawing.
Conclusion
Coconut milk is far more than just a trendy dairy alternative. It’s a culinary staple with a rich history and a diverse range of applications. From its humble origins in tropical cuisines to its current status as a global pantry essential, it brings a unique combination of flavor, texture, and versatility to the table. Whether you’re whipping up a fragrant Thai curry, blending a refreshing morning smoothie, or creating a decadent dairy-free dessert, coconut milk offers a simple way to elevate your meals. While it’s important to be mindful of its high fat content and enjoy it in moderation, its potential benefits and undeniable deliciousness make it a worthy addition to any kitchen.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is coconut milk the same as coconut water?
No, they are very different. Coconut water is the clear, thin liquid found inside young, green coconuts. Coconut milk is a processed product made from the white flesh of mature, brown coconuts mixed with water. It is much thicker, creamier, and higher in fat.
Q2: Is coconut milk healthy?
It can be part of a healthy diet when used in moderation. It contains beneficial MCTs that provide quick energy, but it is also high in calories and saturated fat. The health impact of its specific type of saturated fat (lauric acid) is still being studied. Opt for unsweetened varieties and balance its consumption with a diet full of whole foods.
Q3: Can I use refrigerated coconut milk for cooking curries?
It is not recommended. Refrigerated coconut milk is much thinner and more diluted than the canned version. Using it in a curry will result in a watery, less flavorful sauce. Canned full-fat coconut milk is the best choice for achieving the rich, creamy texture that curries are known for.
Q4: My canned coconut milk is separated. Is it bad?
No, this is completely normal and often a sign of good quality. The thick, solid part is coconut cream, and the thinner liquid is coconut water. Simply stir or shake the can vigorously before opening, or empty the contents into a bowl and whisk to combine them.
Q5: Is coconut milk suitable for a vegan diet?
Yes, coconut milk is entirely plant-based and is an excellent staple for anyone following a vegan diet. It serves as a fantastic substitute for dairy milk and cream in a wide variety of recipes. Always check the label to ensure no dairy-derived ingredients have been added.